SORTIE-ND
Software for spatially-explicit simulation of forest dynamics |
|||||||||||||||
Relative growth behaviorsSeveral behaviors apply a relative growth version of the Michaelis-Menton function. Parameters for these behaviors
Relative growth is calculated with the equation: 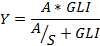 where:
Diameter growth is compounded over multiple timesteps with the equation:
Relative height growth is calculated slightly differently. The details are discussed in the section for the Relative growth - height only behavior below. Relative growth is discussed in Pacala et al 1996. Relative growth limited to radial incrementHow it worksThis behavior calculates an amount of diameter growth according to the relative growth equation. Growth is limited to a maximum of the constant radial growth increment for the species of tree to which it is being applied. The increment is calculated as described in the "Constant radial growth" behavior. Note that the increment parameter specifies radial growth; the behavior makes all necessary conversions. How to apply itThis behavior can be applied to seedlings, saplings, and adults of any species. Any tree species/type combination to which it is applied must also have a light behavior applied. You can use either the diam with auto height or diam only version. Relative growth limited to basal area incrementHow it worksThis behavior calculates an amount of diameter growth according to the relative growth equation. Growth is limited to a maximum of a constant basal area increment. The amount of diameter increase is calculated by dividing the annual basal area increment of the tree's species by the diameter of the tree. The increment is calculated as described in the "Constant basal area growth" behavior. How to apply itThis behavior can be applied to seedlings, saplings, and adults of any species. Any tree species/type combination to which it is applied must also have a light behavior applied. You can use either the diam with auto height or diam only version. Non-limited relative growthHow it worksThe amount of increase returned by the relative growth equation is applied to the tree. How to apply itThis behavior can be applied to seedlings, saplings, and adults of any species. Any tree species/type combination to which it is applied must also have a light behavior applied. Relative growth - height onlyThis behavior uses the Michaelis-Menton function to do height growth. How it worksAfter the Michaelis-Menton function is used to calculate Y as described in the section above, the amount of height growth is calculated as: where:
If the timestep is more than one year long, growth is recalculated for each year of the timestep, increasing the height each time. How to apply itThis behavior can be applied to seedlings, saplings, and adults of any species. Any tree species/type combination to which it is applied must also have a light behavior and a diameter growth behavior applied. |
|||||||||||||||
|
FAQ - Contact Us
|
|||||||||||||||